By KeAi Communications Co.
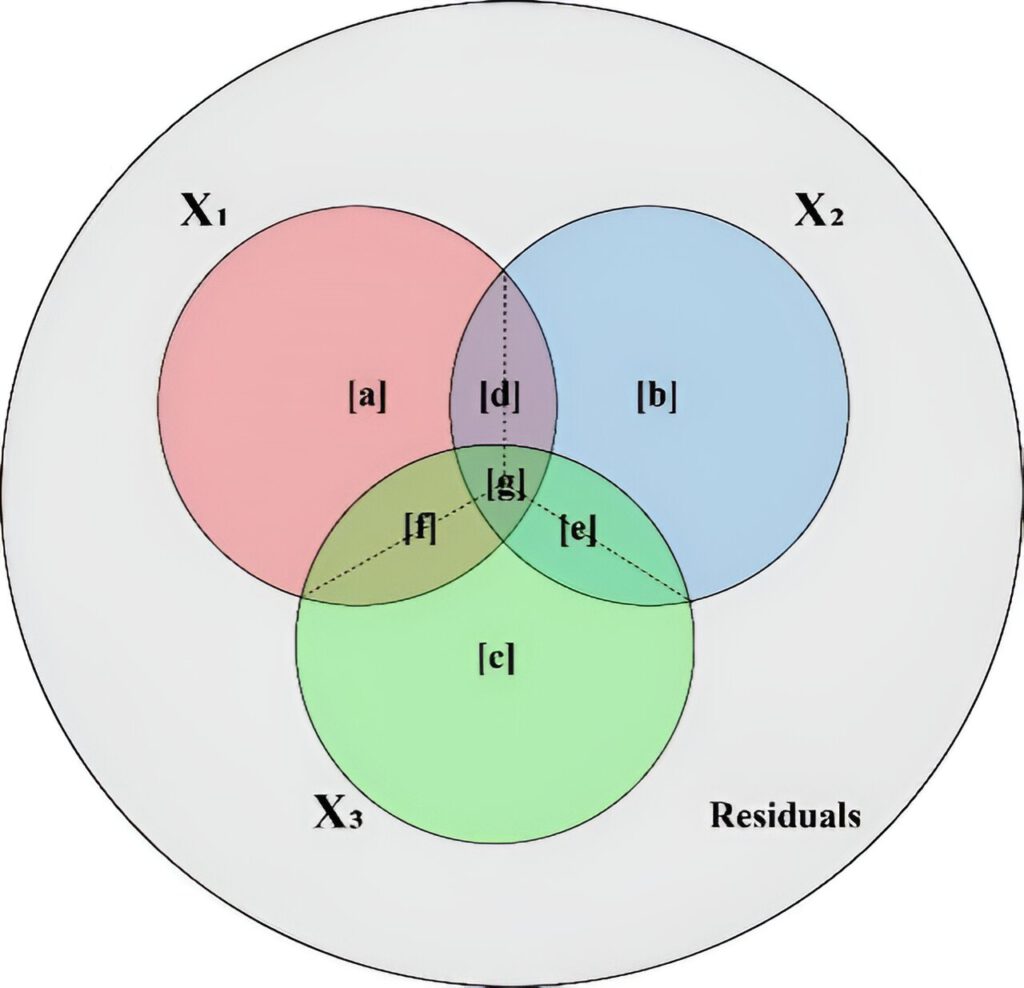
The Venn diagram shows the distribution of the variability components in the generalized additive model. Credit: Jiangshan Lai et al.
Generalized additive models (GAMs) are often used in ecological studies because of their ability to model complex nonlinear relationships; however, overlap in variance between predictors makes it difficult to assess the importance of predictors in the presence of cocurvature.
To that end, a team of researchers from Nanjing Forestry University and Guangzhou Climate and Agriculture Meteorology Center in China created a new computer software package that calculates individual R2 values of predictors based on the concept of “average shared variance,” a technique previously introduced in multiple regression analysis and standard analysis.
“The newly developed gam.hp R package calculates individual R² values for predictors in a GAM based on the concept of ‘average shared variance,'” said Jiangshan Lai, lead and co-corresponding author of the study. “This allows for a fair distribution of the shared R² among relevant predictors, providing a measure of each predictor’s unique and common contribution to the model fit.”
Of note, the gam.hp R package is freely available and details are published in the journal Plant Diversity.
The authors demonstrate the utility of the gam.hp R package by analysing air quality data for London, focusing in particular on the relative importance of emission sources and meteorological factors in explaining variation in ozone concentrations.
Relative importance of individual smoothing variables in explaining ozone concentration variations from gam.hp. Credit: Jiangshan Lai, et al.,
“The findings recommend prioritizing control of NOx emissions during periods of ozone pollution in London, followed by efforts to reduce CO emissions and improve the accuracy of wind speed (WS) forecasts,” Lai explains.
This methodology will support government agencies in formulating more sophisticated and effective strategies for ozone pollution control, taking into account various influencing factors.
“We hope that more researchers will incorporate the gam.hp package into their research. Use this package if its results meet your analytical expectations; if not, it is not mandatory to use it,” Lai said.
More information: Jiangshan Lai et al., “Assessing the relative importance of predictors in generalized additive models using the gam.hp R package,” Plant Diversity (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.pld.2024.06.002
Provided by KeAi Communications Co.
Citation: Free Software Tool Assess Relative Importance of Predictors in Generalized Additive Models (July 22, 2024) Retrieved July 22, 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-07-free-software-tool-importance-predictors.html
This document is subject to copyright. It may not be reproduced without written permission, except for fair dealing for the purposes of personal study or research. The content is provided for informational purposes only.